| CHAPTER 7. WASTE |
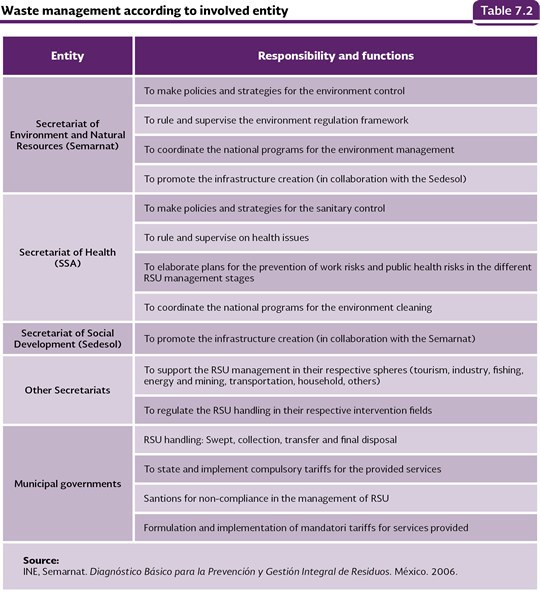
MANAGEMENT OF THE URBAN SOLID WASTE, WITH A SPECIAL HANDLING AND HAZARDOUS In Mexico there are different rules for the regulation; prevention and integral management of waste (see also Box Environmental regulation for waste in the country). In the application of shared responsibility, but distinct, of all the sectors in the prevention and integral management of waste, there are instruments that convey the General Law for the Prevention and Integral Management of Waste, as well as local laws (Mexico City and Guadalajara), among which there are four that are highlighted. The first one of them is the Ruling Programs of Waste Management which propose measures to reduce the waste generation, its separation at the origin source, its collection and transportation, as well as it adequate use, treatment and final disposal. Some examples of the former are National Program of the Prevention and Integral Management of Waste and state and municipal programs of Prevention and Integral Management of Waste (just like in Mexico City, Querétaro and Quintana Roo). In second place, the inventories which works as a support to make decisions to reduce the generation, as well as to provide the indicators about the waste physical state and properties to those who generate, collect, treat or finally dispose the solid waste. The three government levels must elaborate, update and spread the generation inventories of RSU, RP and RME. Besides, they must integrate the inventories of waste dumps or sites where they have been illegally left. In the third place, the waste separation programs, organic and inorganic, in households, companies, merchant, industrial and service establishments, as well as in public and private entities, education centers, government dependencies and the like and their deposit in containers for their collection or recycling by the sanitation public service, in order to ease its use, treatment and final disposal. Finally, the management plans of solid waste must also be noted, by means of which the generators (public, private, social sector) must adopt measures to reduce the generation of RSU and RP, to use those subject to be recycled, re-used or transformed into energy and to treat or confine those which may not get a value. In the problem of waste handling several stages are involved, whose attributions are summarized in Table 7.2.
|